The Cuban ABDALA vaccine arrives in Mexico. Photo: CD Archive
The Revolution celebrates 63 years in an unprecedented scenario, yes, but what does not change is the result: triumph in the face of adversity, resistance in the face of war and the balance undefeated from 1959 to date. I can hardly imagine the size of the embarrassment that the Empire must feel as the years go by without being able to defeat, with all its dollars, that small socialist island that does not account for even 10% of the total population of the United States. What anger. What a shame. And how good.
So, despite the millions coming from the money of the American working class that the White House throws year after year into subversion projects against Cuba, the island goes. The results of Cuban science in the face of covid-19 are the new Playa Girón of the imperialists. What before was defended with rifles, today was won with vaccines.
First Donald Trump and then Joseph Biden tried to take advantage of the terrible health crisis to choke the country’s economy. In a strategy that evoked the sinister Harry Truman, who unleashed the atomic nightmare on Japan in order to “save lives”, these presidents occupied the pandemic to sow unrest with the aim of promoting the counterrevolution. And again, they failed.
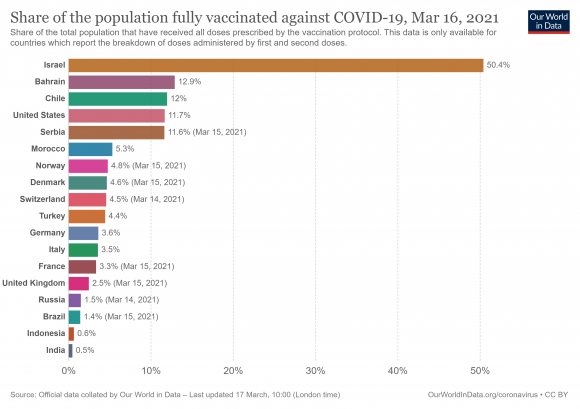
Today, Cuba is one of the few countries in Latin America and the world to vaccinate its entire population. With two exceptions: the island also vaccinated its children and did so with its own vaccines.
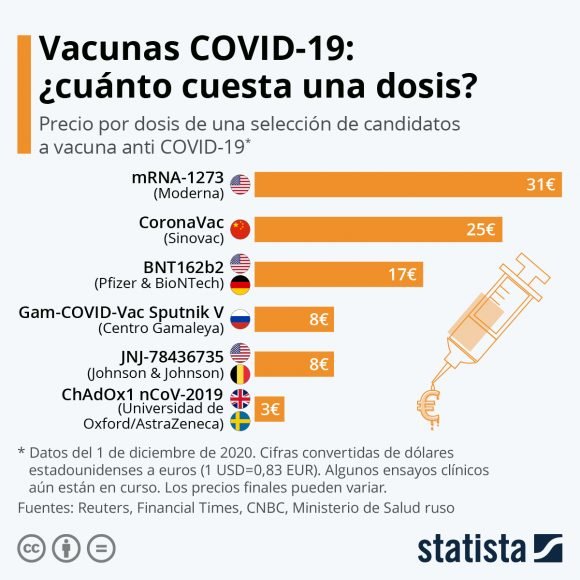
Indeed, unlike nations like Mexico, which met the goal with imported biologicals, the largest of the Antilles forged its solutions. In this way, the country is about to sell to the Government of Andrés Manuel López Obrador a good shipment of doses of Abdala, the work of the Center for Genetic and Biotechnological Engineering that has astonished the world.
At the end of December, the Federal Commission for the Prevention against Sanitary Risks (Cofepris), of the Mexican Ministry of Health, approved the use of Abdala. In 2022, many people in Mexico will be vaccinated with the fruit of revolutionary medical science, just as they will in other countries such as Venezuela or Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.
The repercussions of this news are great. It is the most influential country in the Latin American continental area, placing the Cuban biological in the same range of the Pfizer or AstraZeneca vaccines (something that the prestigious magazine The Lancet had already done ).
The event constitutes a blow to the ego of the Empire which, for months, has tried to undermine the prestige of the island laboratories. And a hard lesson to the media monopolies that continued the post-truth game by attacking vaccines made in Cuba. It is therefore expected that many more countries will join this example.
For Mexico, the use of Abdala is a very important reinforcement in its fight against covid-19. The country has made an effort to immunize the majority of its population over 15 years of age, and it has succeeded, but, in its eagerness, it has had to deal with the governments of the United States and Europe, as long as there are no shortages of immunizations. A painful case happened to him with Russia, a country that never complied with the shipment of 25 million Sputnik vaccines, forcing the federal government to negotiate even more with Washington.
So Abdala will help supply the necessary arrests that López Obrador has had to carry out in obtaining biologics, buying Cuban vaccines at a lower price, with results equal to or greater than their US and English counterparts.
Even following the example of Havana, the country could vaccinate boys and girls, which it has not been able to do since only the Pfizer dose is approved for that purpose. Thus, the friendship between Mexico and Cuba scores another success.
(Taken from From Below MX )




 By Randy Alonso Falcón, Cuban journalist, Director of the web portal Cubadebate, the site Fidel Soldado de las Ideas and the Cuban Television program “Mesa Redonda”. He directed other Cuban publications such as Somos Jóvenes, Alma Mater and Juventud Técnica. He received the Juan Gualberto Gómez National Journalism Award in TV in 2018. He has won several awards in the 26th of July National Journalism Contest. Email:
By Randy Alonso Falcón, Cuban journalist, Director of the web portal Cubadebate, the site Fidel Soldado de las Ideas and the Cuban Television program “Mesa Redonda”. He directed other Cuban publications such as Somos Jóvenes, Alma Mater and Juventud Técnica. He received the Juan Gualberto Gómez National Journalism Award in TV in 2018. He has won several awards in the 26th of July National Journalism Contest. Email:  Edilberto Carmona Tamayo, Chief of the Department of Multimedia Production, Monitoring and Innovation of Cubadebate and the Roundtable. Graduated in Journalism in 2016 from the University of Holguín. Contact:
Edilberto Carmona Tamayo, Chief of the Department of Multimedia Production, Monitoring and Innovation of Cubadebate and the Roundtable. Graduated in Journalism in 2016 from the University of Holguín. Contact: 
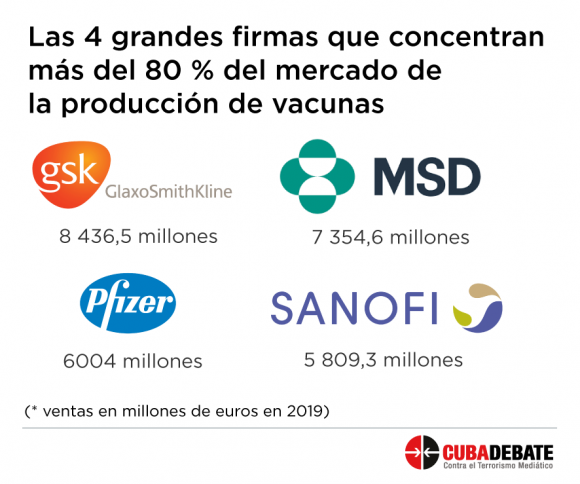










 Luis Alberto Cabrera Montero holds a Doctorate Chemical Sciences. He is a Senior Researcher and Full Professor at the University of Havana. He is President of the Scientific Advisory Council of the University of Havana and is a Merit Member and Coordinator of Natural and Exact Sciences of the Academy of Sciences of Cuba. For a full biography, see
Luis Alberto Cabrera Montero holds a Doctorate Chemical Sciences. He is a Senior Researcher and Full Professor at the University of Havana. He is President of the Scientific Advisory Council of the University of Havana and is a Merit Member and Coordinator of Natural and Exact Sciences of the Academy of Sciences of Cuba. For a full biography, see 
You must be logged in to post a comment.