Cuba 13
Vaccination against selfishness and inequality

Vaccination against selfishness and inequality
By: Randy Alonso Falcón
January 27, 2021
Translated and edited by Walter Lippmann for CubaNews.
 “It will not be an exhausted and outdated world order that can save humanity and create the indispensable natural conditions for a dignified and decent life on the planet. (…) This is not an ideological question; it is already a question of life or death for the human species.”
“It will not be an exhausted and outdated world order that can save humanity and create the indispensable natural conditions for a dignified and decent life on the planet. (…) This is not an ideological question; it is already a question of life or death for the human species.”
Fidel Castro Ruz
Speech at the Open Tribune of the Revolution, held in San José de las Lajas
January 27, 2001
Solidarity and Justice are still words in disuse even when the catastrophe concerns us all, like a great universal Titanic. A tiny and sticky virus has moved fears, shaken societies and health systems, provoked countless reflections on today and the future, but it has not succeeded in making equity and love for others prosper.
This week will mark the 100 millionth person infected with COVID-19 in the world and already more than 2 million people have died.
“Every day the gap between the haves and have-nots grows. The pandemic has reminded us that health and economics are linked and that we are all in the same boat. The pandemic will not end until it ends everywhere,” said World Health Organization Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus on Monday.
The numbers bear incontrovertible witness to the expert’s assessment.
The privileged cure

Despite numerous calls from the UN and various world leaders to seek a global response to the pandemic and to facilitate and share access to a cure for the disease, narrow views and deaf ears predominate.
“Science is succeeding, but solidarity is failing,” UN Secretary-General António Guterres noted on January 15. Several vaccines are already available worldwide to tackle the SARS-CoV-2 virus, but access to them is as deeply unequal as the world we inhabit.
Some 66.33 million doses have been administered to date, 93% of which were delivered in just 15 countries: the US, China, UK, Israel, United Arab Emirates, Germany, India, Italy, Turkey, Spain, France and Russia, according to the data analysis platform Our World in Data, based on figures from Oxford University.
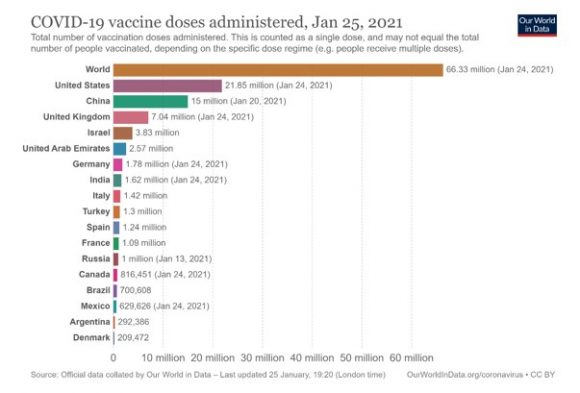
In all of sub-Saharan Africa, only 25 doses of vaccine could be administered in Guinea. Populous countries like Nigeria, with 200 million inhabitants, are waiting for the first dose.
The same scramble that took place at the beginning of the pandemic with lung ventilators, masks and protective suits is now being staged with vaccines: hoarding, overpricing and speculation. “An immoral race to the bottom,” as the WHO’s top executive described it.
The COVAX fund, created as a sort of global effort to make vaccines accessible to the poorest nations or those with limited resources, announced that in February it will begin to deliver the first doses (they first said that in January), but it recognizes that it has been limited by the lucrative agreements of various individual nations with the pharmaceutical companies that produce the anti-COVID vaccines.
Another handicap has been the high cost of the vaccines that have the most international approval so far. As Norwegian expert John-Arne Rottingen told The Guardian, “The difficulty is that we really only have widespread international approval for marketing two vaccines: the two mRNA vaccines. The challenge is that one, the Moderna vaccine is very expensive, and the other, the Pfizer / BioNTech vaccine, which was first available and is now being applied in Europe, is moderately expensive compared to others, and requires a super cold chain. The price and cold chain makes it not the ideal vaccines for a global vaccine.”
While nations like India and South Africa are calling on the WHO to campaign for pharmaceutical companies to relinquish intellectual property rights to COVID-19 vaccines and treatments. That would allow other qualified manufacturers in the South to expand production of those antidotes; countries like the US, UK and Canada have opposed the initiative. Those three wealthy nations have purchased or reserved enough doses to inoculate their populations at least four times.
High-income countries account for 16% of the world’s population, but hold more than 60% of the vaccines purchased so far.
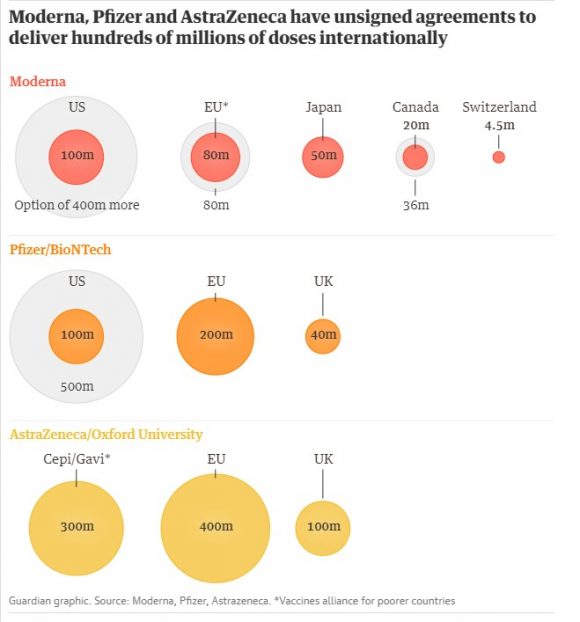
Rich countries account for the lion’s share of vaccine production. Graphic: The Guardian
Some forecasts put the total population of middle-income and poor countries that could be vaccinated this year at 27%. Duke University’s Center for Global Health Innovation estimates that there will not be enough vaccines to immunize the world’s population until at least 2023.
“The world is on the brink of a catastrophic moral failure, and the price of this failure will be paid in lives and livelihoods in the world’s poorest countries,” Dr. Tedros regretfully sentenced.
The virus of inequality

“Vaccine nationalism” is the exact reflection of an unequal and unjust world in which a few remain the great beneficiaries of wealth, for which billions must make do with the leftovers.
It is the “inequality virus” that OXFAM denounces in its most recent report, in which it evidences that the current failed economic system “allows a super-rich elite to continue to accumulate wealth in the midst of the greatest economic crisis since the Great Depression, while billions of people face great hardship to get by.”
While billionaires saw their fortunes increase between March and December 2020 by a total volume of $3.9 trillion-to amass an unimaginable $11.95 trillion-the poorest people on the planet will need “more than a decade to recover from the economic impacts of the crisis” accentuated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Racial differences have also deepened. In the United States, the most powerful nation on the planet, if mortality rates were equal to those of the white population, nearly 22,000 Latinos and blacks would not have died from the coronavirus outbreak. In Brazil, people of African descent are 40% more likely to die from COVID than whites.
One of the conclusions of the Oxfam report is that “the pandemic is likely to increase inequality in a way never seen before”. The World Bank has warned that, in the current context, more than 100 million people could reach extreme poverty.
The 10 richest men in the world saw their net worth increase by $540 billion in the pandemic 2020 period. That list is topped by Jeff Bezos and Elon Musk. It also includes luxury group LVMH CEO Bernard Arnault, Bill Gates and Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg. According to Oxfam, the money hoarded by these potentates would be enough to prevent people from falling into poverty due to the effects of the virus and would also guarantee a vaccine for everyone on the planet.
Sunshine of the moral world

Among so much inequity and indifference, a small archipelago in the Caribbean, called Cuba, has been able to send thousands of doctors and nurses, in some 50 brigades of the “Henry Reeve” Internationalist Contingent, to more than thirty countries in Latin America and the Caribbean, Europe, Africa and the Middle East, to collaborate in the fight against the deadly disease.
Thousands of lives saved or recovered in a scenario of total complexity are the fruit of their solidarity work. The human and professional quality of these sons and daughters of the Cuban people overcomes the most diverse obstacles. It leaves a mark of affection, gratitude and example that is recognized by all those with whom they have shared and whom they have cared for.
That same country, with scarce economic resources but abundant in trained and educated talent, has been able to build an advanced biopharmaceutical industry, which is now preparing to produce 100 million doses of Soberana 02, one of the 4 vaccines on which its scientists are working. This would make it possible to immunize the entire Cuban population (it would be one of the first countries to achieve this) and to have more than 70 million doses available for other peoples of the South. There are already countries interested in acquiring it, such as Vietnam, Iran and Venezuela, Pakistan and India, the Director General of the Finlay Vaccine Institute recently announced.
Researchers from that institution are working with countries such as Italy and Canada to test the impact of the Soberana 01 vaccine on people who have already had COVID-19 and are convalescing, but are at risk of reinfection.
“We are not a multinational where (financial) return is the number one reason. We work the other way around, creating more health and return is a consequence, it is never going to be the priority,” Dr. Vicente Vérez, leader of the main vaccine research center in Cuba, explained to the press last week.
“Our world can only beat this virus one way: united,” the UN Secretary-General recently emphasized. Unfortunately, the vaccines of solidarity and justice have not been able to be applied in the rich world that dominates.
MYTH: “If the Cuban revolution is so good….

MYTH: “If the Cuban revolution is so good, Cubans living in the U.S. and defending it should return to Cuba
 Author: Dr Salvador Capote
Author: Dr Salvador Capote
January 3, 2021
Translated and edited by Walter Lippmann for CubaNews.
 REALITY:
REALITY:
The decision to live in the United States is an individual one and is made for one or more of many reasons that are part of a freedom of conscience that no one, especially those who lack the necessary authority, can question. Hundreds of thousands of Cubans live in the United States who wish to establish civilized relations between this country and Cuba, to be able to travel freely to the island and to send help to their families.
Within this sector, there are many who defend the humanist character of the revolution, its achievements and triumphs, its immense effort to achieve a system of equality and social justice, its solidarity, without this necessarily meaning that they assume, in their totality, the revolutionary principles, methods and objectives.
A considerable part of the Cuban population in the United States has already put down deep roots. They have established or rebuilt their families. They have children, grandchildren, nephews, etc., born here, and only someone who is very blinded by rancor, very ignorant, very insensitive, or very irresponsible, can demand that, for ideological reasons, they abandon them and return to live in Cuba.
To a great friend and comrade, Michael Martínez, born in the United States of Cuban parents, a union leader, in a demonstration demanding the cessation of hostility against Cuba and Venezuela, a television journalist publicly asked the well-known question: If the Cuban revolution is so good, why don’t you go and live there? Mike’s answer was, in my opinion, the best of all: “I am not going to live in Cuba because it is here, in the United States, where the Revolution must be made.”
Maintaining links with the Homeland is completely normal. What is not normal is that someone, who calls himself a Cuban, supports the criminal blockade against Cuba, advocates intensifying the economic strangulation of his own people, tries to prevent the reunion of families, promotes the execution of terrorist acts on the homeland and shows himself – in his visceral hatred – a supporter of an invasion of Cuba by the Marines, even though he knows that they will only collect “the dust from his blood-soaked soil,” as Antonio Maceo warned.
But since it is a question of questioning, why not question the hundreds of thousands of Americans who, also for multiple reasons, have established their place of residence abroad? Why, if the United States is paradise, do so many go to live in Costa Rica, the Dominican Republic, Mexico? and it is possible to find them in practically any corner of the planet? This, without going into the subject of occupation troops, CIA stations, secret prisons and military bases all over the planet.
Finally, and without trying to exhaust the subject, although the Cuban government has the decency not to use the fact as propaganda, every year there are thousands of Cubans who, in spite of all the difficulties, return to Cuba for the permanent and definitive reunion with their identity and their roots.
United States declines, China progresses

United States declines, China progresses
By Hedelberto López Blanch
October 14, 2020
Translated and edited by Walter Lippmann for CubaNews.
After the economic-social debacle represented by the expansion of the Covid-19 pandemic through almost all the nations of the world, the People’s Republic of China, where the virus was detected for the first time, has managed to raise its economy while that of the United States continues to fall.
The specialists assure that this great difference between the two main economic powers of the world is due to the fact that China, from the first moments, took the pertinent measures to control the disease, in contrast to the United States whose President Donald Trump dismissed the seriousness of the virus.
The North American retreat has been occurring since the last decade and it increased with the appearance of the coronavirus, fundamentally due to the laziness of its officials to face it.
Several data point out the weaknesses of the American giant because despite being a power with very important resources and capabilities for the welfare of most of its inhabitants, their real wage today is lower than 40 years ago.
Under that premise, the average employee must work twice as many years as three decades ago to pay the price of a small apartment.
The level of inequality has progressively worsened among the population with stagnation of real wages compared to the cost of living. Almost 50 million people are below the poverty line and 36% of Americans lack the health insurance that gives them access to specialized health care.
In the last decade, suicides increased 24% and at the same time life expectancy decreased to only 76.10 years. In Cuba, a developing country economically and financially blockaded by Washington, that rate is 78.2 years.
Recently the Department of Commerce reported that the country’s economy contracted in the second quarter of 2020 at the fastest rate in its history and represents the biggest debacle since World War II.
According to the Department’s Bureau of Economic Analysis, real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) declined at a rate of 32.9 percent in the second quarter of 2020 due to the disastrous effects of the pandemic. In the first quarter, it was minus 5 percent.
The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) estimated a 7.3% drop in US GDP for 2020, a figure that could be altered if the coronavirus wave is sustained or increased.
Meanwhile, China emerges as the powerhouse that will end the year of the pandemic with positive economic growth. If in the first quarter its GDP was at minus 6.8%, in the second quarter it grew by 3.2%, exceeding all analysts’ forecasts.
The National Statistics Office of the Asian giant indicated that “in the second quarter growth went from negative to positive”, in a context of economic recovery after the stagnation caused by the coronavirus and that “the market outlook is generally good”.
In nominal terms, China’s total wealth in the first half of the year stood at 45.66 trillion yuan ($6.53 billion).
For the Beijing government, the health policy adopted throughout the nation has been fundamental, through which it has been able to control covid-19, even in asymptomatic people.
Since August 16, no local infections have been recorded and only imported cases have been detected, people who immediately go into a 14-day quarantine.
Of course, this way of stopping the proliferation of the disease contrasts with those applied in the United States and other Western nations. A free health-care policy has been essential to achieving this.
The IHS Markit agency reported that exports represented 20% of the global total between April and June, seven percentage points more than in the same period in 2019, and also applied the alternative of increasing domestic consumption among its large population.
The Asian giant’s recovery has been influenced by the rapid digital transformation of its economy, which was growing strongly before the pandemic, and which accelerated with it.
In 2018 it already represented 34.8% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), a percentage that grew year after year above the growth of the Product.
Zhang Jun, dean of Fudan University’s School of Economics and director of China’s Center for Economic Studies, explained that families, unable to leave their homes, adopted applications such as JD.com, Meituan, Eleme and Pinduoduo for daily product purchases.
The companies took advantage of digital tools, from communication platforms such as Enterprise WeChat and DingTalk to electronic contracts, to keep their businesses running.
The end result has been that China is on its way to an economic revival, while in the United States there is still no light at the end of the tunnel.
Subscribe to Blog via Email
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | |||||



You must be logged in to post a comment.